Considerations for Safety and Beef Quality Assurance
Introduction
Using proper injection techniques for animal health products, including reproductive hormones, helps ensure these products can work effectively. In addition, we need to safely handle animals and health products to protect both farm workers and animals.
The Injection Site
Follow Beef Quality Assurance recommendations for injection site placement when administering reproductive hormones. Today, her primary purpose is milk production, but nearly all dairy cattle will have a “second career” producing meat. For this reason, Beef Quality Assurance (BQA) applies to dairy producers just as it does to beef producers. BQA covers aspects of animal care and health (including the use and administration of animal health products), transport, and more. Whenever possible, injections should be placed in economically less important cuts of meat. In cattle, this means the side of the neck and avoiding the hindquarters (Figure 1). When the label allows for it, administering products subcutaneously (SQ; under the skin) also reduces the risk of tissue damage.
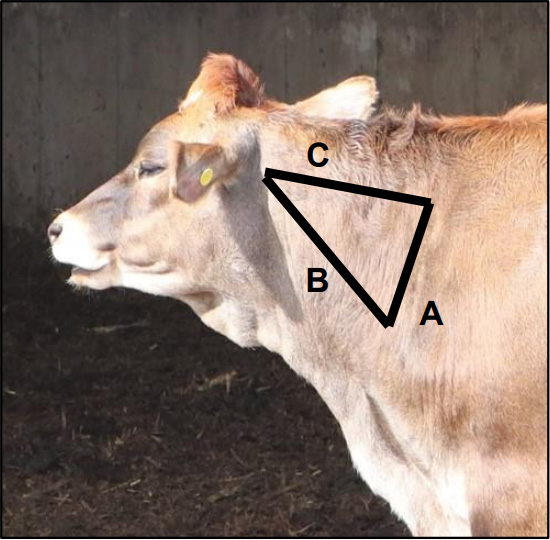
A = Ahead of point of shoulder
B = Above the vertebrae
C = Below Nuchal Ligament
Photo credit: Ryan Sterry)
Be smart with needles. Needles are intended to be single-use. Whenever possible, use new needles for each animal. This reduces the risk of disease transmission between animals. If reusing needles, never reuse a bent needle. Using a bent needle increases the risk of a needle breaking. Replace needles that develop a burr at the tip. Burred needles increase resistance to piercing the skin, create more tissue damage, and increase the risk of needles breaking. If reusing needles, they should be replaced after 10-15 injections.
If a needle breaks in an animal, try to recover it. If it cannot be recovered, identify on the animal’s records the approximate area where the broken needle was left. These cattle should be harvested locally by processors who can carefully trim the area around the broken needle.
Needle selection. Needles are available in a wide range of gauges (diameter) and lengths. Correct needle size is based on animal weight, the product’s viscosity (thick vs. thin), and route of administration (SQ, intravenous, and intramuscular). BQA guidelines recommend using 18 to 16 gauge, ¾ to 1-inch-long needles for intramuscular (IM) or ½ to ¾ inch long needles for SQ injections. The longer the needle, the greater the risk of it breaking. However, the needle must be long enough to ensure the injection is placed deep enough in the muscle. Selecting a needle diameter that is too large increases the risk of the product dripping out of the injection site and down the animal’s hide. Needle diameters that are too small may be too fragile to pierce the hide without breaking or bending the needle, and may result in having to use too much force on the plunger to deliver the product.
Injection site lesions can occur when an injection site becomes infected. Lesions can result from damaged tissue, or the formation of abscesses at the injection site (accumulation of dead cells, fluids, and pus). Using properly sized, clean (new) needles, and making sure the injection site is clean can help reduce the incidence of injection site lesions. Injecting less volume of a product can help to minimize the formation of a lesion, therefore it is important to consider dose volumes of comparable products, using those that require less volume per injection.
It is also important not to insert a used or dirty needle into a medication bottle. Instead, always use a new needle or a transfer needle when filling syringes to prevent product contamination. Pistol grip syringes must be taken apart and properly cleaned after use and stored in a clean, dry place between uses.
Spread multiple injections apart by 4 inches (a hand’s width) or have a protocol for which side of the neck is to receive which product (ex., right side of the neck for GnRH and left side for prostaglandin). For example, you do not want to inject GnRH into the exact same area that may be irritated because of a recent prostaglandin injection. Irritated tissue and lesions will interfere with hormone absorption. Most synchronization protocols require multiple injections, and over her lifetime, a cow may undergo several rounds of synchronization. This may cause scar tissue to form, reducing the available area within the injection triangle.
Safety
It has been common practice in the dairy industry to administer injections in the hindquarters of cattle. Convenience and safety are the reasons for doing so. As compared to their heads, the hindquarters are better restrained while cows are in freestalls, headlocks, palpation rails, or tie stalls. Attempting to administer an injection in the neck area without first haltering the head is dangerous and can result in injury. However, we are learning that farm workers can safely administer products in the neck injection zone while dairy cattle are restrained in headlocks. The location where farm workers can safely reach through to administer neck injections depends on the headlock style. In Figure 2, we show two different styles used in dairy facilities. Workers must avoid pinching or injuring their arm by the swinging bar portion of the headlock, or by a cow swinging her head.
Prevent needlestick injuries. Again, be smart with needles. Studies have shown that up to 80% of dairy and livestock farm workers have experienced an accidental needlestick injury. Three steps farm workers can take to prevent injury include: 1) take time and carefully handle needles and reproductive hormones; 2) properly restrain animals before attempting to administer injections, and 3) use proper equipment and techniques. This includes using caution while removing needle caps, recapping used needles, and properly disposing of needles.
Warnings and Precautions. The label will contain a section on warnings and precautions for the user (human), animal, and any residue warnings for meat and milk. Dinoprost and cloprostenal (i.e. prostaglandin) labels typically contain a warning statement for women of child-bearing age, asthmatics, and persons with bronchial and other respiratory problems about using these products. They are readily absorbed through the skin and may cause abortion and/or bronchospasms. Accidental skin contact must be washed off immediately with soap and water. Handlers need to have access to and be aware of where wash areas are located.
Wearing nitrile gloves helps protect farm workers handling reproductive hormones. This includes wearing protective gloves when handling non-injectable reproductive hormone products, such as Controlled Internal Drug Release (CIDR) devices containing progesterone.
Headlock Style Number 1
✅ CORRECT
Arm placed through fixed position bars of headlocks, where swinging bar cannot injure it.
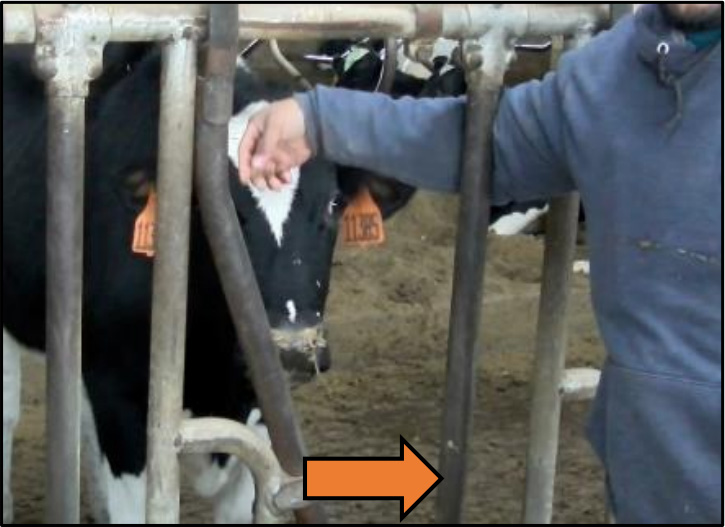

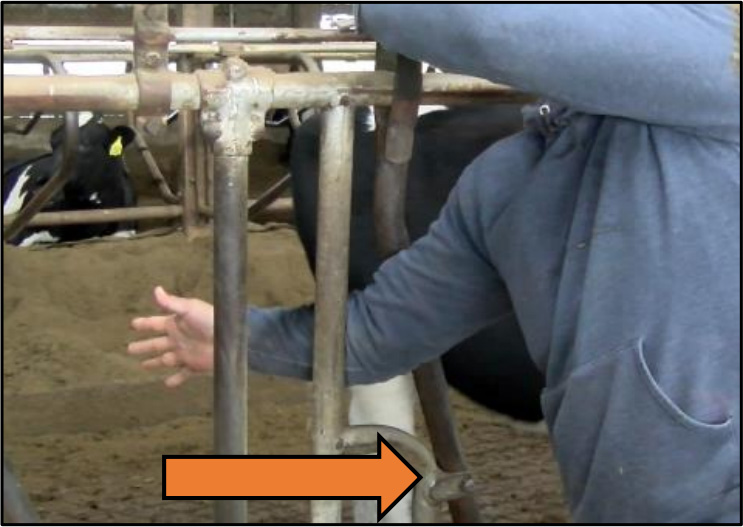
❌ INCORRECT
Arm placed through area where swinging bar of
headlocks can move and pin it, causing injury.

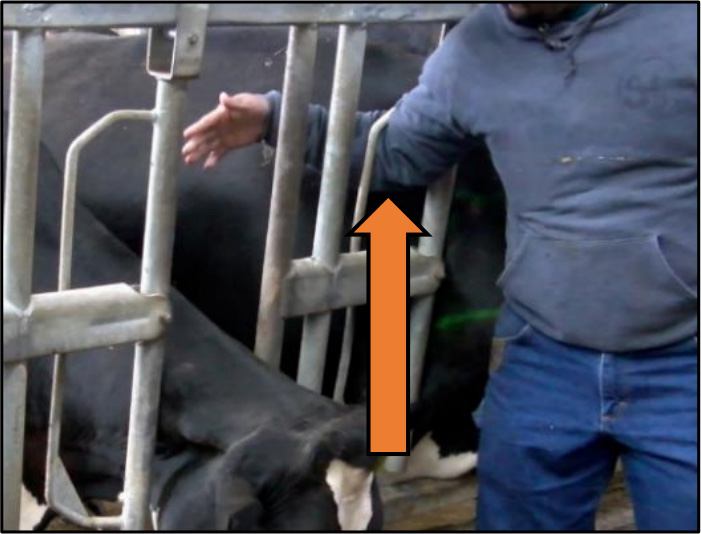
Headlock Style Number 2
✅ CORRECT
Arm placed through swinging bar, through the pivot point guard bar, where it cannot swing all the way back on the farm workers arm.

❌ INCORRECT
Arm placed through area where swinging bar of
headlocks can cause injury.
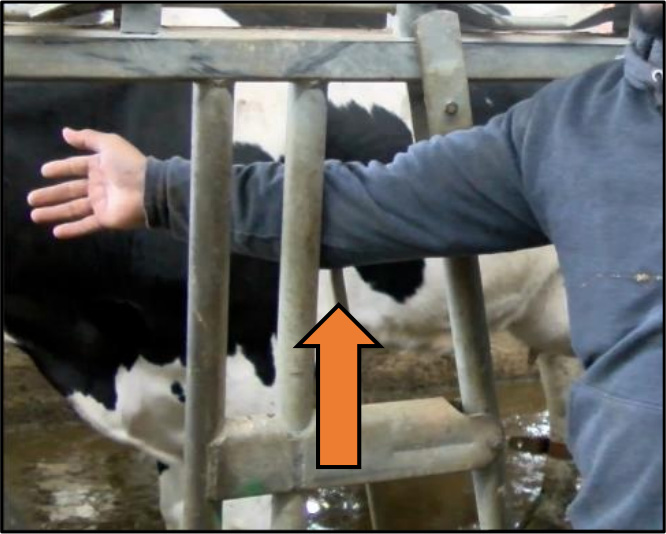

(Figure 2. Areas for farm workers to reach, and not reach, through headlocks.
Photo credits: Heather Schlesser)
Labeling & Records
Follow the label. The label is a legal document manufacturers provide with every product. It’s the responsibility of the user to follow the label’s directions for use, route of administration, dosage, withholding periods, and safety precautions. The label will also contain storage information and expiration dates. If the product was issued under a veterinarian’s prescription, refer to that veterinarian with any questions or follow-up care.
Keeping accurate and current records is important to ensure the right animals receive the right injection at the right time. Failure to follow protocols, by administering the right injection to the right animal at the right time, is one of the leading causes for reproductive management programs to have poor results.
Keeping a record of the product name, lot number, and route of administration is important if tracing is ever required. Tracing will occur if questions are raised about the efficacy of a particular batch of product, or if adverse reactions occur in an animal.
Authors

Ryan Sterry
Regional Dairy Educator / Professor – Ryan Sterry is a Regional Dairy Educator and Professor with the University of Wisconsin – Madison, Division of Extension. With a home office in St. Croix County, Ryan serves Barron, Pierce, and St. Croix Counties. His educational programming and research focuses on dairy management, cattle reproduction, and Beef x Dairy crossbreds.

Heather Schlesser
County Dairy Educator – Heather Schlesser is an Agriculture Educator in Marathon County. Heather’s research and outreach have included the use of current technology to enhance farm profitability and sustainability. Her current projects include the Animal Wellbeing Conference, the Midwest Manure Summit, Beef Quality Assurance, financial programming, and teaching farmers throughout the Midwest how to breed their own cattle.
Sandy Stuttgen
County Livestock Educator
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Extension
Bill Halfman
Beef Outreach Specialist
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Division of Extension
Published: July 19, 2023
Revised: January 16, 2026
References
- Monthly Safety Blast. Tyler, TX: The Southwest Center for Agricultural Health, Injury Prevention, and Education, 2016 Jun; https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/216103
- Villarino, M. A. (2009) Proper Injection Techniques in Dairy Cattle, Texas A&M AgriLife Extension. https://agrilifeextension.tamu.edu/asset-external/proper-injection-techniques-in-dairy-cattle/
- Beef Quality Assurance Field Guide https://www.bqa.org/Media/BQA/Docs/bqa_field-_guide.pdf