Table of Contents

Introduction
UCLA’s John Wooden is known for his unparalleled run as men’s basketball coach, winning 10 national championships in a 12-year period. He is equally well known outside the sporting world for the Pyramid of Success™, his list of 25 personal traits and characteristics that lead to personal and team success.
Today, we can form our own pyramid of characteristics for high performing dairy herd reproductive management. During a recap of the 2024 Reproduction Roadshow, Dr. Paul Fricke, Dairy Cattle Reproduction Specialist for UW-Madison and Division of Extension, introduced his building blocks for top reproductive performance and how achieving each step opens more opportunities to use additional reproductive technologies.
Fricke’s Hierarchy of Reproduction Needs
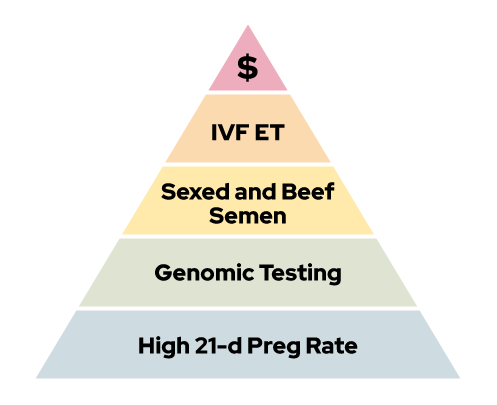
Pyramid of characteristics for high performing dairy herd reproductive management
(Pyramid Visual Concept: Dr. Paul Fricke)
Block 1: High 21-day pregnancy rates
This brings us to our first building block: achieving high 21-day pregnancy rates. How you get there depends on your management style and environment.
For example, tools like Double Ovsynch have been proven to not only synchronize cows for Artificial Insemination (AI) but can also be used to improve fertility. Likewise, more and more activity monitoring products are reaching the market, yet another tool in the toolbox to alert management to cows in estrus.
The key is your herd’s 21-day pregnancy rate must be the foundation.
Block 2: Genomic Testing
The next building block, genomic testing, is less beneficial if the 21-day pregnancy rate isn’t solid.
Why? If cows are not becoming pregnant the negative hit becomes twofold. More cows will become reproductive culls, necessitating the need to raise more replacement heifers. At the same time, fewer heifer calves are being born simply because fewer cows become pregnant and calve in again. Your herd will quickly return to a cycle where every heifer calf stays, regardless of their genetic potential, because every one of them will be needed to make the milking string and maintain herd size.
Block 3: Sexed and beef semen
Having and using genomic and performance data to inform breeding decisions is necessary to reach the third block, optimizing the use of sexed and beef semen.
As we achieve greater reproductive success, more doors open to use these technologies. Through strategic use of sexed semen, you can determine which dam’s are most worthy of producing the next generation in your herd. Management gains more control over the number of heifer calves born annually, and some cows can be bred to beef for inventory management and to maximize the market value of non-retained calves. Cows on the lower end of genetic potential can become recipients of beef semen. Finding the right mix of sexed and beef semen for your herd is a different topic, but the point remains if fertility isn’t managed, there is no opportunity for management to make those breeding choices.
Block 4: Invitro Fertilization (IVF) and Embryo Transfer (ET)
Closely related to beef semen and sexed semen technology is the use of Invitro Fertilization (IVF) and Embryo Transfer (ET). Not only can we select which dam’s will produce replacements, but truly elite individuals can produce multiple offspring. Possibilities exist to produce full blooded beef calves in place of crossbred calves. Herds are experimenting today with using no conventional semen, achieving the pregnancies they need through a mix of sexed semen use, beef semen, and IVF / ET.
Block 5: Success
There is no reason today not to reach the pinnacle, with more tools available than ever before to improve fertility and submit cows for AI in a timely manner. When fertility is poor, fewer opportunities exist to use sexed semen, beef semen, or IVF and ET because the focus returns to “we just need to get cows pregnant.” Conventional semen again becomes the tool of choice to manage conception rates and for cost control. It’s easy to get caught up in the hype of what beef x dairy crossbred calves
Reviewer
Dr. Paul Fricke
Dairy Cattle Reproduction Extension Specialist, Professor
University of Wisconsin-Madison and Division of Extension
Author

Ryan Sterry
Regional Dairy Educator / Professor – Ryan Sterry is a Regional Dairy Educator and Professor with the University of Wisconsin – Madison, Division of Extension. With a home office in St. Croix County, Ryan serves Barron, Pierce, and St. Croix Counties. His educational programming and research focuses on dairy management, cattle reproduction, and Beef x Dairy crossbreds.



 Single Gene Traits in Dairy Cattle
Single Gene Traits in Dairy Cattle ▶️ Watch: Strategies for improving reproduction in dairy herds
▶️ Watch: Strategies for improving reproduction in dairy herds Renovating Tie-Stall Barns for Indoor Calf Housing
Renovating Tie-Stall Barns for Indoor Calf Housing Effects of Heat Stress on Dairy Reproduction
Effects of Heat Stress on Dairy Reproduction