Articles
Strengthening biosecurity practices on dairy farms
The careful implementation of biosecurity practices is key to protect both people and animals, as well as to ensure a viable and safe food supply for consumers.
▶️ Watch: Strategies for keeping calves cool in hutches
Jennifer Van Os discusses collaborative work at UW-Madison to identify practical strategies for alleviating heat stress in hutch-housed dairy calves.
▶️ Watch: Understanding the carryover effects of early life heat stress on dairy calves
his presentation will explore how heat stress affects the physiological, behavioral, and developmental aspects of calves during their critical early stages of life and highlight the long-lasting implications that persist into adulthood.
Mooving Cows: Learn basic cow handling skills to stay safe and keep cows calm
Mooving Cows™ is an educational game where you can practice moving cows around a dairy farm. Learn about cow behavior and practice basic cow handling skills to stay safe and keep cows calm.
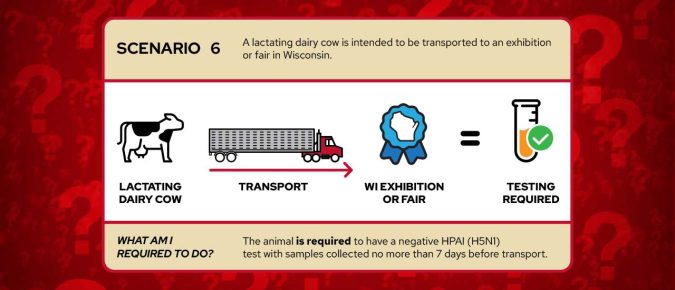
Am I required to test for HPAI (H5N1) before transporting my cattle?
The Federal order regarding the HPAI (H5N1) virus situation requires testing for specific interstate (across state lines) travel of lactating dairy cattle. Read about different scenarios to assist farmers with understanding the Federal order.
▶️ Watch: Basic Biosecurity Practices For Livestock Operations
This video focuses on basic biosecurity practices for livestock operations.
▶️ Watch: Biosecurity Practices For Livestock At Fairs, Shows, And Exhibitions
This video outlines practices for biosecurity at fairs, shows, and exhibitions.
▶️ Watch: Biosecurity During a Disease Outbreak
This video provides an overview of biosecurity during disease response.
Water: A critical and undervalued nutrient in dairy calves
Water contributes to 75 percent of the body weight in calves, making this nutrient an essential daily requirement.
Proper semen handling for improved fertility in bovines and other livestock
Proper semen handling requires being comfortable with a liquid nitrogen tank so you can work quickly and effectively to avoid damaging frozen semen.
Heat Stress Abatement in Dairy Facilities
When cows are heat stressed, they eat less, produce less milk, have reduced immune function and higher SCC, and show reduced fertility. A spike in lameness often follows the hot season.
Animal Handling During Heat Stress
Combating heat stress in the herd requires an action plan to prevent heat stress and address heat stress-related issues.