Dr. Theresa Ollivett, Associate Professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison School of Veterinary Medicine, dives into the hidden challenges of respiratory disease in young dairy calves.
By looking beyond visible symptoms, this technology equips farms with the insights needed to make proactive, data-driven decisions that support long-term calf health, productivity, and welfare.
Mastitis is one of the most common and economically impactful diseases in dairy cattle and remains a top priority in both conventional and Automatic Milking Systems (AMS).
En esta charla discutiremos cómo la implementación de programas intensivos de alimentación a terneras de reposición durante las primeras semanas de vida mejora su crecimiento, de qué forma afecta su desarrollo ruminal y su potencial productivo futuro.
Cattle herds in Wisconsin face ongoing challenges from two species of liver flukes—Fasciola hepatica (the common liver fluke) and Fascioloides magna (the deer liver fluke). These parasitic flatworms can cause significant liver damage, reduce animal productivity, and increase the risk of secondary infections, such as Redwater Disease.
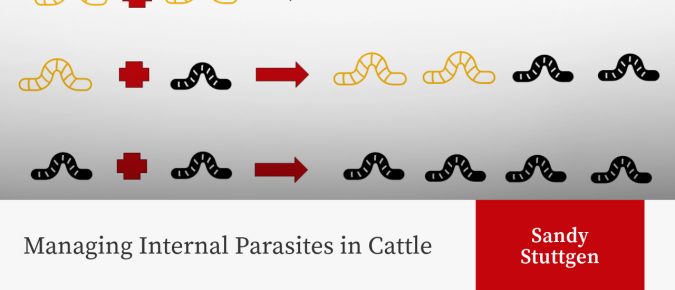
“On behalf of intestinal helminth parasites everywhere, I would like to thank dairy and beef producers for hosting us in their cattle and on their pastures this summer. Despite your management efforts, we reproduced inside your cattle.”
Deworming is beneficial for beef and dairy operations, provided it is done correctly with effective products. However, due to anthelmintic resistance, relying solely on dewormers is insufficient.
Bovine leukosis infection in cattle, like PFAS chemicals, is almost universal in dairy herds. Yet, unlike PFAS, we don’t have to resign ourselves to living with it; we can take specific steps toward its control and elimination
The presentation provides an overview of Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV) including the biology of the virus, impacts on cattle health and production, diagnostics, and control.
Calves born with knuckle over pasterns, also known as contracted tendons, present a unique challenge for dairy and beef producers.
Lameness issues impact every dairy herd in one form or another. Not only does lameness affect a cow’s health and well-being, but it’s also costly to the farm’s bottom line.
Milk fever (hypocalcemia) is a common disorder than can occur is cows following calving. During this time, the demand for calcium in the body is high to support mammary function and milk production. When a cow is unable to meet these demands, she can develop milk fever.